The most important management of rice in July is to increase production and see here!
In July, rice entered the long-earth stage, which is the key period for determining rice yield. During the summer and summer, it is high temperature and rain. It is necessary to deal with the contradiction between individuals and groups, the growing environment and rice, material production and distribution, so that they can develop harmoniously, and achieve strong stalks, large ears, large grains, fullness, and prevention of greed. Lodging, pests, cold damage and other purposes. Since this time is about 30 days, the rice grows fast and the management indicators are many. It is necessary to strengthen the field management, especially the prevention of low temperature and cold damage, in order to ensure safe heading to win high yield.
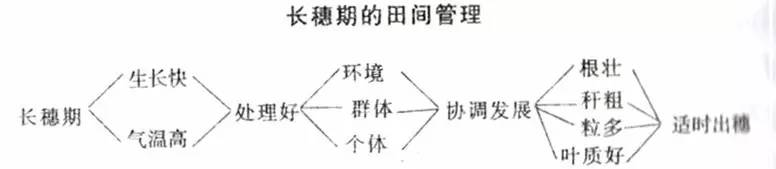
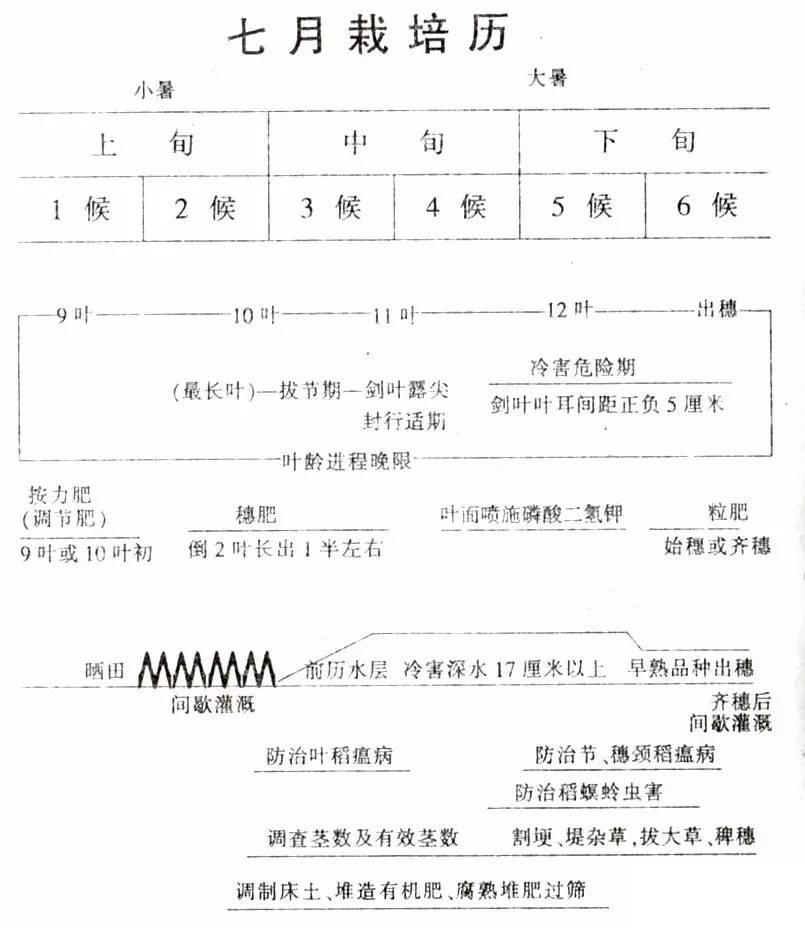
First, the leaf age process of rice in the long ear stage
The long ear stage begins at the end of June and the beginning of July, and is generally around 30 days from the beginning of August. Including four leaf age periods, taking 12 leaf varieties as an example, the first four leaves of the inverted four leaves (ie, 9 leaves) at the end of June and early July, the inverted three leaf branches and stems (10 leaves) before and after the small heat (July 8) Inverted 2 leaf spikelet differentiation (11 leaves) around July 15th, the inverted 1 leaf meiosis period (sword leaves) was extracted in the heat (July 23), after 1.2 leaf age (about 9 days) The heading is reached and the safe heading is achieved.
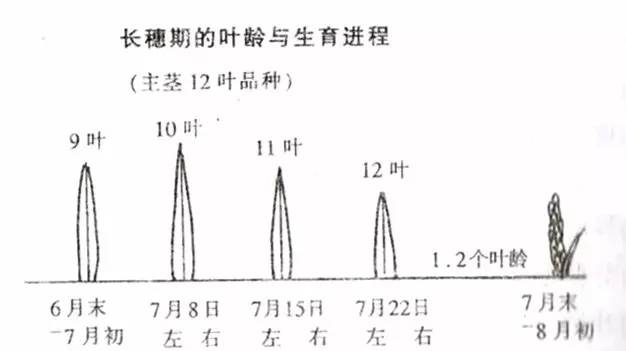
Second, rice long-term fertilizer application
The purpose of panicle fertilizer: mainly to increase the number of spikelets and prevent their degradation, to lay a good foundation for safe and timely seeding, and to improve the seed setting rate and grain weight.
Application time and method:
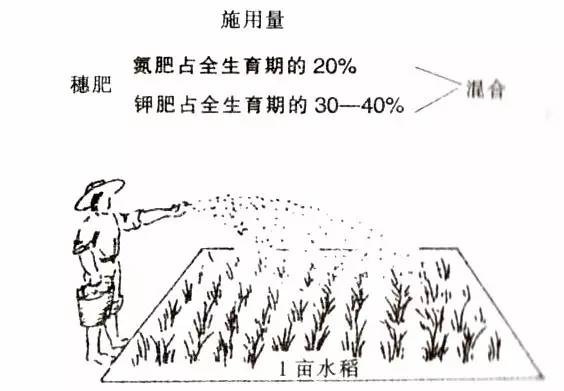
Panicle fertilizer is generally applied 20 days before heading. The application of panicle fertilizer is applied when the penultimate 2 leaves grow about half, so that the effect of the floret differentiation and meiosis is observed to prevent the degradation of the floret and enlarge the volume of the glume. According to the overall fertilization design, the amount of nitrogen fertilizer is 20% of the total growth period, and the potassium fertilizer dosage is 30-40% of the total growth period.
Precautions:

In the middle and late July or the booting stage before heading (after the leaves of the flag leaf are extracted), according to the leaf color and disease measurement report, potassium dihydrogen phosphate and rice vinegar can be sprayed to promote heading, increase the seed setting rate, and increase the grain weight.
Second, rice long-term irrigation management
At this stage, there is a delay in the field or due to the delay of the tiller. The friends who are preparing to work in the field will take control of the time and discretion. Intermittent irrigation should be adopted in the first ten days of July to supply oxygen to the soil, so that the root system will be deep-lined. No root rot will occur, and deep nutrients in the soil will be absorbed, and no fattening or premature aging will occur. Intermittent irrigation in shallow water is to inject 3~5 cm of water layer at a time, block the nozzle, and dry it to the surface of the water. When the foot is still a little water, it is filled in the water layer of 3~5 cm. It needs to be repeated.
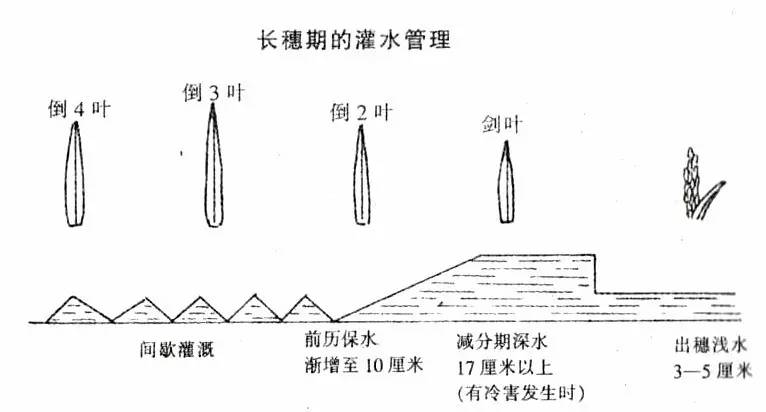
At about July 15 (11 leaf varieties), when the flag leaf is partially extracted, the water layer is about 10 cm, and the water temperature in the well irrigation area should be raised to above 18 °C to prepare for the defensive obstacle cold damage. During the period of plus or minus 5 cm, that is, within the range of 8 to 14 days before the earing, if there is a low temperature below 17 °C, the water layer should be increased to more than 17 cm, and the defensive obstacle is cold. In the future, shallow water irrigation will be resumed. If there are plots with too much fertility and deep leaf color, 4 to 5 days before heading, the field can be properly dried or sun-dried.
4. Prevention and control of pests and diseases in rice long-earning stage
Disease
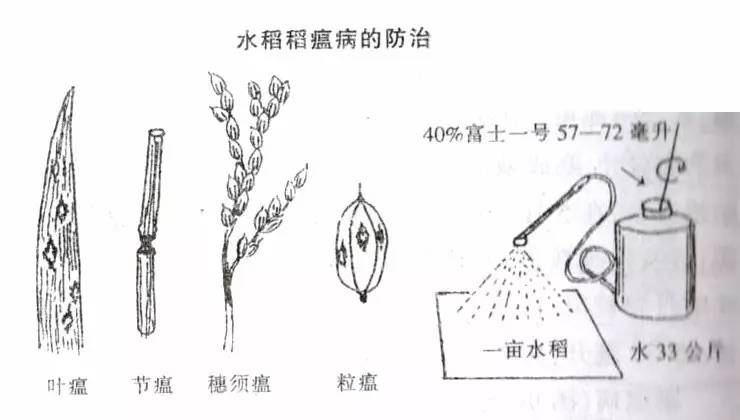
The main disease of rice in the long-earning stage of Heilongjiang Province is rice blast. After the leaf blast, thrift and panicle scorpion will appear in the middle and late July. For the overgrown fields, we will continue to prevent and control them in a timely manner according to the weather changes.
2. Pests
There are mainly rice blasts, also known as rice worms, blue-necked locusts, and scorpion worms. They occur in the middle and late July to the middle of August. The larvae hide in the middle and lower parts of the rice groves during the day, and damage the rice in the evening. The newly hatched larvae feed along the veins. The mesophyll forms white streaks. When the larva matures, it will sew and fold at the tip of the rice leaf, and form a scorpion-shaped triangular leaf scorpion. Then the bite will fall into the field and the stalk will eventually become adult.
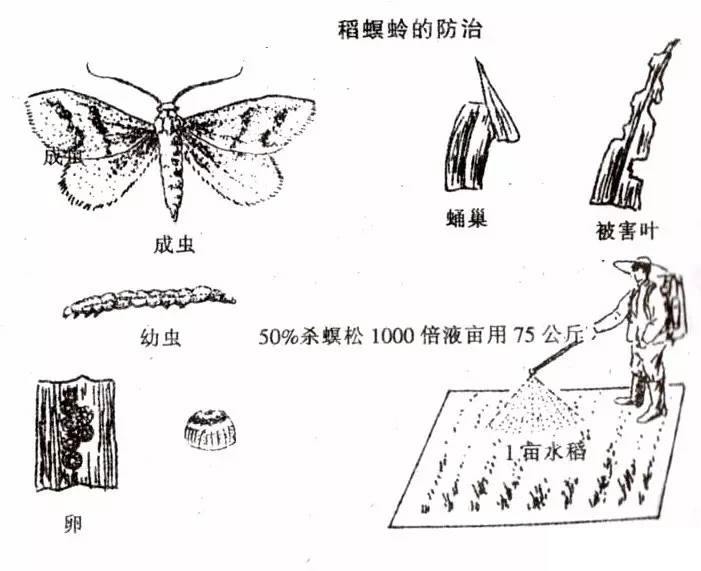
Control measures: use light to trap moths, eliminate insect-bearing straw, eliminate wintering insects, apply pesticides before and after the third instar, use 2.5% kungfu emulsifiable concentrate 10~20 ml per acre, or 50% mites pine emulsion 1000 Double liquid, or 40% dimethoate emulsion 1000 times liquid, spray about 75 kg per mu.
3. Weeding
Even if the field weeding operation in the long ear stage is over, the weeds on the residual weeds and dikes cannot be ignored.
It is necessary to remove the large grass and hoe in the field in time, cut off the weeds on the ridge and the levee, prevent the weeds from spreading repeatedly to avoid the breeding of the bacteria, and create good ventilation and light transmission conditions for the rice.
Lung Function Instrument Mouthpiece
Lung Function Instrument Mouthpiece,Plastic Disposable Mouthpiece,Medical Paper Mouthpieces,Disposable Paper Mouthpieces
Hengshui Qifei Paper Products Co. LTD , https://www.hengshuiqifei.com