Local delivery of tumor immunological checkpoint inhibitors by microneedle patch
Release date: 2016-11-18
Tumor immunotherapy is one of the most exciting areas in the development of anticancer drugs. For example, the strategy of blocking the activation of immunosuppressive receptors on T cells is used to enhance T cell function, and the immune checkpoint-T-cell programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) blocking antibody has been approved by the FDA for treatment. Late melanoma. However, the current overall response rate of PD-1 inhibitors in patients is still relatively low, which may lead to immune-related adverse reactions such as inflammation. In addition, inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is also important for the regulation of the immune system. The IDO pathway helps tumor cells escape the surveillance of the immune system by inhibiting the activation of T cells by down-regulating the body's immune capacity.
Recently, Prof. Zhen Gu, from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and the Department of Biomedical Engineering at North Carolina State University, and his team published a research paper on ACS Nano to deliver PD1 and its technology through microneedle patch technology. IDO immunological checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of melanoma tumors significantly control tumor growth.
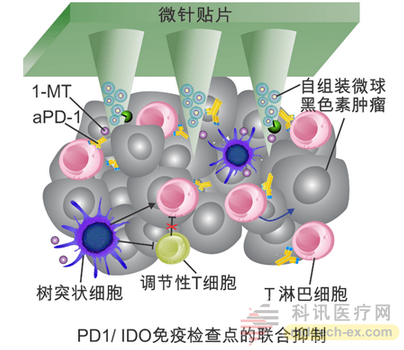
The researchers co-assembled the small molecule IDO inhibitor anticancer drug 1-MT with hyaluronic acid and self-assembled into microspheres in aqueous solution, while encapsulating PD-1 antibodies. "This drug-loading strategy of encapsulating A drug in a carrier constructed from drug B not only provides the possibility of co-administration, but also enhances the overall drug-loading capacity," said Yanqi Ye, the first author and Ph.D. student. ) explained. This technology enables the sustained release of the drug through the presence of an enzyme that cleaves hyaluronic acid in the tumor microenvironment, reduces the body's peripheral immune tolerance to tumor-specific antigens, and enhances the immune system's selectivity for cancer cells. Killing function. In a mouse tumor model, this method of local combination therapy effectively activates tumor-invasive effector T cells, thereby significantly controlling tumor growth. This co-administered immunomicroneedle patch achieved 70% tumor-bearing mouse survival compared to the single treatment method.
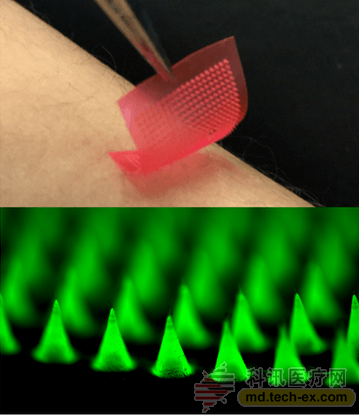
Dr. Chao Wang, co-author of the study, said: "This patch has clinical implications for early and middle-stage skin tumors, and can effectively inhibit tumor growth and prevent it from spreading to other organs before surgery." In recent years, 臻Lab has developed a number of new formulations that respond with physiological signals and combined with microneedle devices to achieve transdermal smart drug delivery, including “smart insulin patch†and PD-1/CTLA-4 combined immunotherapy patch. Wait.
 
Â
Http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsnano.6b04989
Introduction to Professor Gu Wei: http://
The research team website: http://
Source: X-MOL
Erythritol For Baking,Fruit Erythritol,Xylitol Of Erythritol,Xylitol Powdered Erythritol
Ningxia Eppen Biotec CO.,LTD , https://www.nxeppen.com