How many ears of corn will harvest?
Maize multi-spike refers to the fact that there are more than two spikes on a single plant of corn, and they cannot be normally fruited or have very few seeds and become a phenomenon of no-effect spikes. In recent years, frequent occurrence of multiple spikes (ineffective spikes) in corn has severely affected the yield and quality of corn, and individual farms even harvested individual fields.
Maize multiple ear blast shape?
The first is "finger spike." At the same stem section (leaf) in the middle of a corn plant, multiple spikelets grow at the same time, resembling finger-like, basically without seeds, often referred to as "finger spikes", and others as "banana ears."
The second is a single stalk and more ears. In the middle of the corn plant, more than 3 different stem segments (leaves) grow 1 to 2 spikelets, respectively, resulting in multiple non-effect spikes on the single plant in corn.
The third is more stalks and more ears. In the same stem section of the corn plant, additional plants were planted, and multiple non-effected ears grew at the stem sections (leaves) of the tiller plants.
Causes of multiple ears of corn?
Multiple spikes are determined by the biological characteristics of corn. In addition to the top 4 to 6 nodes of common maize, there are axillary buds on each node, ie, the ear primordium, and the axillary buds on the non-extensive stem of the main stem will form tillers. Axillary buds on Long Festival will differentiate the ear. Under normal circumstances, only the upper 1 or 2 axillary buds can differentiate the ear, but in the case of excess nutrients, it will stimulate the differentiation and development of 3 to 5 axillary buds, forming a phenomenon of multiple spikes (Some maize varieties, under suitable conditions Axillary buds will develop into panicles at the same time, often with 2 to 3 ears or even more per plant. The ear of corn is botanically a metamorphic lateral stem. The stem of the ear is a shortened stem. Each section of the stem has a petiole-only metamorphic leaf (leaf lobe), and a certain number of axillary buds are lurking in the leafhopper. If the spindle is dead and more nutrients are accumulated, these axillary buds will also sprout and develop into multiple spikelets.
Under normal circumstances, corn rarely produces multiple ears and produces multiple spikes, which are related to the following factors:
(1) Genetic properties. Some varieties are vulnerable to external environmental conditions and produce more than one ear. According to relevant reports, hybrid corn is more likely to produce more ears than conventional corn.
(2) Bad weather. The harsh climate that easily leads to multiple ears is mainly severe drought and low-temperature sunshine.
Maize is a short-light crop, if the severe drought in the ear and ear differentiation stage, will cause the spindle spindle to stop development, so that the latent buds on the ear stem (short stems) germinate and develop "finger spike." When the “finger spike†is drawn, the tassels arrive at the loose powder stage, at which point no pollen supply is available, and the firmness is poor.
The low temperature, continuous rain, and lack of light will lead to insufficient organic nutrition of the corn plants, poor silking of the female flowers or failure of normal flowering of the tassels, affecting pollination and fertilization, resulting in failure of the first ear to form a spike. Therefore, excess Nutritional supply The development of the next ear, if the second ear is still unable to pollinate normally, nutrition will provide the next development of the ear. Even if the ear develops normally in the late period, no pollen can be given in the field. Therefore, they cannot be solid and produce multiple spikes.
(3) Dashui Fertilizer. Fertilizer and Dashui are one of the reasons for the formation of multiple spikes in corn. In the stage of maize ear differentiation, if the water and fertilizer are sufficient, excessive nutrient material plants cannot be consumed, and multiple axillary buds on the stem section will germinate and develop, and there may be the formation of multiple spikes. If the loose powder meets the rain, the pollen of the pollen will not be pollinated normally, and it will also cause the phenomenon of multi-filament empty culm.
(4) pests and diseases. If corn suffers from rough dwarf disease, the stimulant produced by the virus will break the hormone balance in the plant, resulting in the loss of the ear position of the first female ear, promoting the germination of other axillary buds and forming many spikelets. The earlier the disease, the more obvious the phenomenon of multiple ears. In addition, corn borer, aphids and corn leaf spot disease and other hazards will also affect the normal formation of corn ear, resulting in multiple ear phenomenon.
(5) Improper cultivation and management. During the development stage of maize, the supply of fertilizer and water is too large, which promotes the development of multiple spikes of multiple female inflorescences. The excessive planting density results in the closure of the field, poor pollination, and abnormal development of the ear, which promotes the development and maturation of other axillary buds and the formation of multiple spikes.
Multi-spike prevention of corn?
1. Based on local conditions, select corn varieties that are not susceptible to multiple spikes.
2. Timely sowing, scientific cultivation. According to characteristics of corn varieties, local climate, planting season, plots and other reasonable sowing time (avoiding drought, low temperature and other illegitimate weather and other adverse weather), sowing volume (reasonably dense planting, maintaining ventilation and light transmission between plants, improve light energy utilization Rate), whether to cover the film, etc., so that the light, temperature, and water and fertilizer indexes required by each corn growth stage are met.
3. Focus on fertilizer management. According to the growth and development rules of maize, it is necessary to grasp the fertilization time and amount of fertilization, apply basic fertilizer, apply Miaofei lightly, and apply jointing fertilizer. Compound fertilizer is used as base fertilizer, phosphorus and potassium fertilizers are applied early, and nitrogen fertilizer is applied at seedling stage, jointing stage, respectively. Appropriate application at the tapping stage. Sufficient moisture is supplied during tasseling and flowering to prevent drought. Timely cultivating and weeding to keep soil loose.
4. Strengthen pest control. Timely prevention of corn borer, aphids and corn leaf spot disease, corn rough dwarf disease, etc., to prevent the emergence of multiple ears of corn due to pests and diseases.
5. Remove ineffective spikes in time. During the silking stage, multi-spike plants were found and should be actively organized to remove excess fruit spikes as early as possible. Only one or two spikes were reserved for each corn to avoid consumption of nutrients, promote normal growth of the ear, and reduce loss.
Ready-to-eat Sweet Corn Kernels
In one sunny morning, a sweet corn or glutinous corn is a good choice for breakfast to kick-start the day. Corn has a richer taste than other staple food. Glutinous corn has a sweet and waxy taste. It's also a filling food to fill up for the day, supplement the nutrition that the human body needs.
Fruit corn. The outer leaves are pale green, and the inner grains are white or yellow.The sweetness is higher than sweet corn, but the starch content is low, rich in vitamin E and cellulose, can fight aging and help digestion.Ideal for raw food, mixed with vegetables into salad;It can also be steamed, but don't cook it for too long, about five minutes.


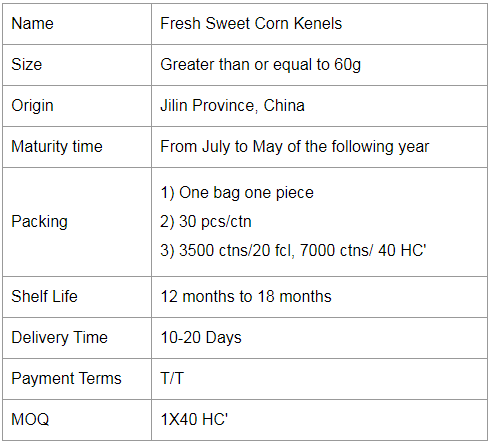
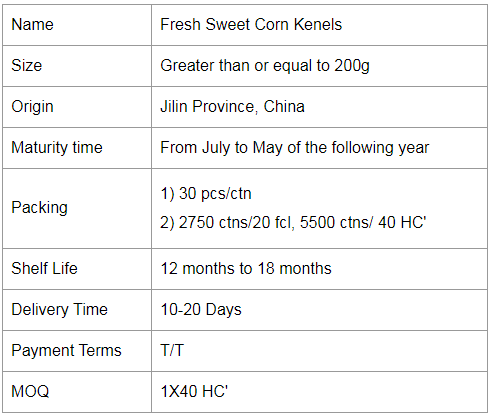
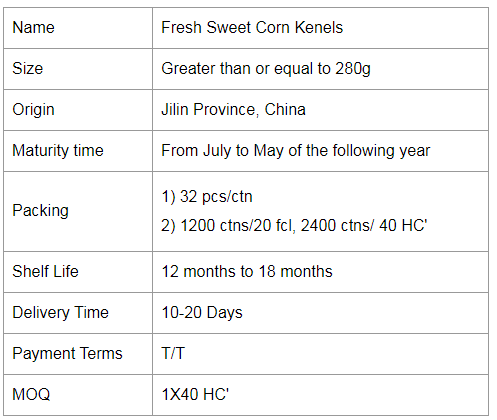
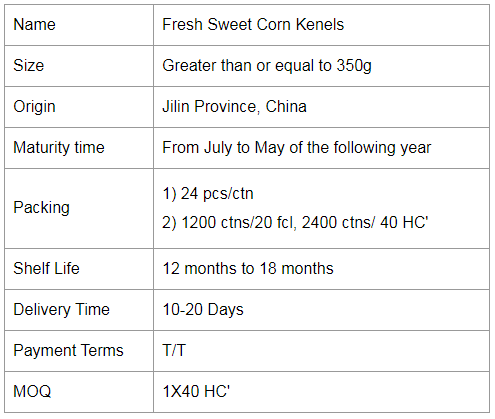
If you would like to work with us, please send us a message on the website or contact us by email.
Fresh Corn Kernels,Corn Whole Kernel,Boiled Corn Kernels,Baby Corn Kernels
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorn.com