Innovative technologies in the quality control of international vaccine companies
Since the inventor of our ancestors, Jenner, invented vaccinia, today, in the course of more than two hundred years of history, the development of vaccines has undergone several revolutions, and each time the corresponding research results have been applied to resist And cure diseases and defend human health. Today, the application of vaccines not only effectively controls or eliminates certain severe infectious diseases, but also is widely used in the prevention and treatment of diseases such as family planning and cancer, autoimmune diseases, immunodeficiency, and hypersensitivity reactions. It is indisputable that the vaccine has made a great contribution to human health protection, quality of life improvement and social development.
Vaccines can be classified according to the process: live vaccines (attenuated vaccines); inactivated vaccines; subunit vaccines; genetically engineered vaccines, etc.
Because of the complex structure of the vaccine and the difficulty of the process, quality control is particularly important.
Quality control at least guarantees:
1. Security
a) the product itself: such as the neurotoxicity of the attenuated vaccine
b) Process introduction: such as lysing agents for influenza vaccines, antibiotics
c) Process residue: product residue, external pollution
d) late addition: preservatives, stabilizers, adjuvants, etc.
2. Effectiveness
a) Confirmation of active ingredients
b) Determination of content
c) Determination of potency
3. Stability: indicators after preservation of the preparation
4. Consistency: batch-to-batch variation
Due to a variety of factors, most domestic manufacturers still use traditional manual methods for quality control, which is easy to introduce errors due to excessive manual operations. In addition, the method is backward. For the emerging genetic engineering recombinant vaccine, the traditional method may not accurately describe the quality attributes of the recombinant vaccine. The advanced quality control methods adopted by some foreign vaccine companies are reviewed for reference.
Immunological identification
Immunological identification is a very important means of detecting active ingredients. EIA, ELISA, and protein gel are widely used in current quality control. EIA, the method of ELISA, because there is no molecular weight information, can not fully explain protein integrity and so on. Protein glue, because of too many manual operations, it is easy to introduce too much error.
A large number of Merck vaccine studies have used the ProteinSimple Simple western system for immunological identification of vaccines.
Simple western repeatability
 Immunological identification of tetravalent C. difficile vaccine
Immunological identification of tetravalent C. difficile vaccine
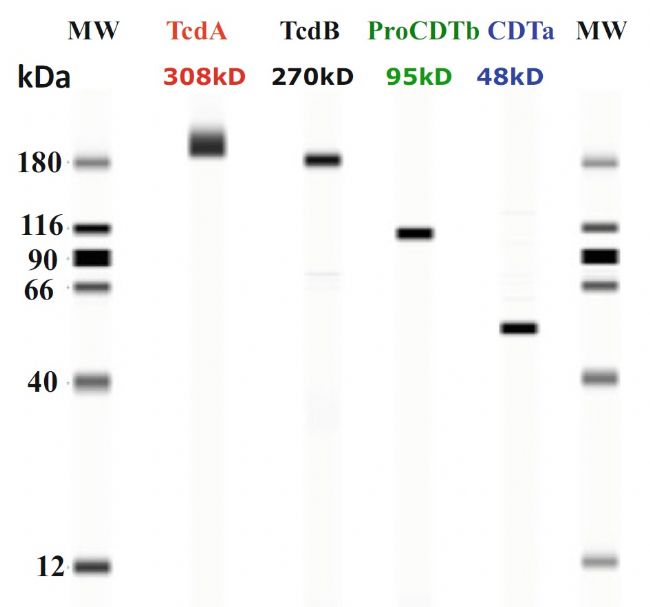
Applications of an Automated and Quantitative CE-Based Size and Charge Western Blot for Therapeutic Proteins and Vaccines, Capillary Electrophoresis of Proteins and Peptides: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 1466,2016
Immunological identification of 15-valent pneumococcal vaccine
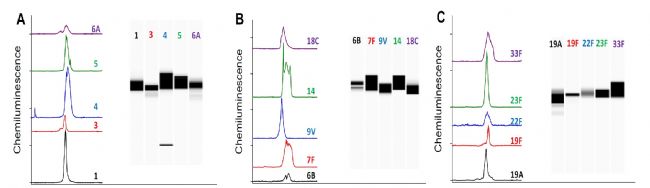
References: Automated capillary Western dot blot method for the identity of a 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, Anal. Biochem. (2015)
2. Vaccine isoelectric point detection
Isoelectric points are important for vaccine process development. For example, purification using ion exchange chromatography (IEX) is based on product and contaminant charge differences, formulation buffer selection and product precipitation are all related to isoelectric points.
Example of isoelectric point detection:
Polio test for live poliovirus
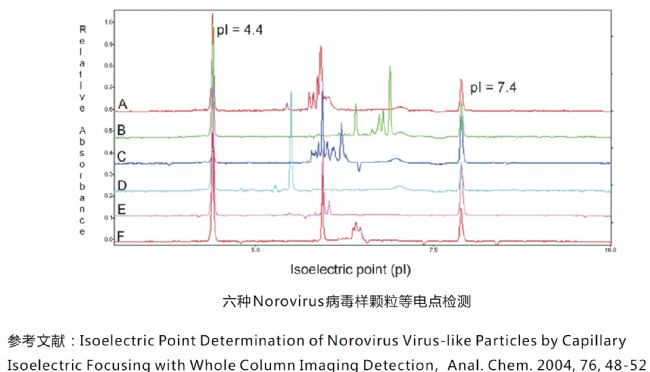
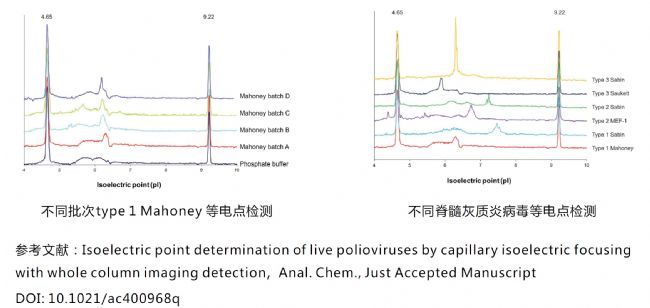 Virus-like particle isoelectric point detection
Virus-like particle isoelectric point detection
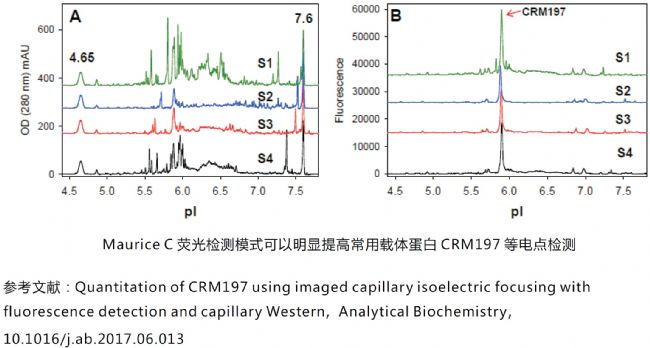
 Combined vaccine carrier protein detection
Combined vaccine carrier protein detection
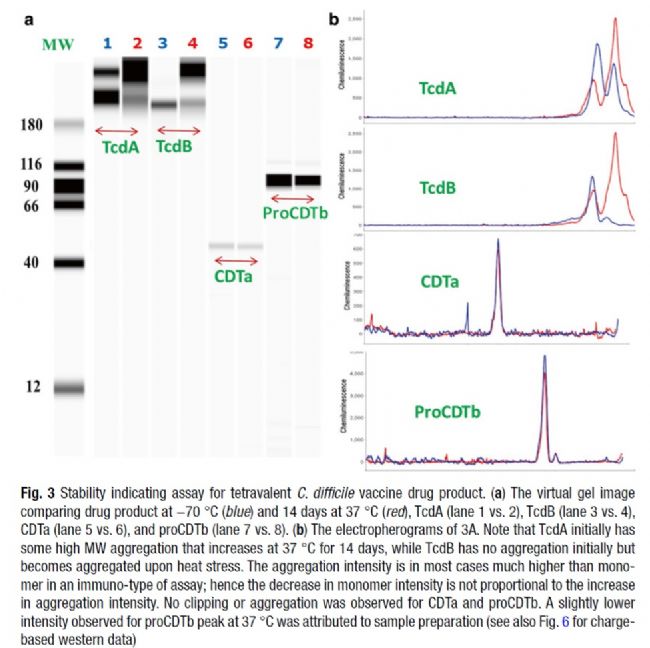
3. Stability test
1) In the investigation of vaccine stability, molecular weight change detection indicates protein degradation or protein aggregation
Bottom: Merck's tetravalent C. difficile vaccine stability study, large molecular weight antigens TcdA and TcdB aggregated at 37 °C for 14 days.
 2) Different buffer stability investigation, the isoelectric point reflects the stability change. As shown in the figure below, the three kinds of buffers of HBsAg are recombined and freeze-thawed repeatedly, and the product in bufferA is stable.
2) Different buffer stability investigation, the isoelectric point reflects the stability change. As shown in the figure below, the three kinds of buffers of HBsAg are recombined and freeze-thawed repeatedly, and the product in bufferA is stable. 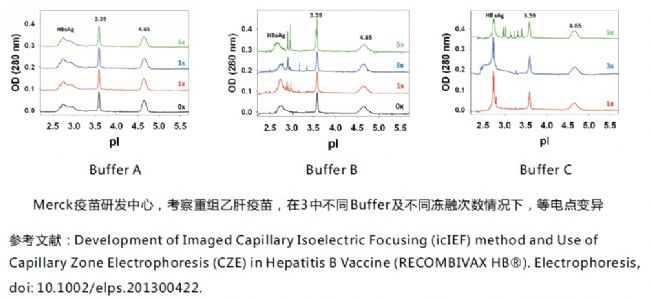
A medium-sized cob of corn provides more than 10% of our daily dietary fibre requirements.
There are two types of dietary fibre - soluble and insoluble - and sweet corn contains both.
According to the American Heart Association, dietary fibre as part of an overall healthy diet can help lower blood cholesterol levels and may reduce the risk of heart disease. It is insoluble fibre that binds to cholesterol, preventing it from being absorbed into the bloodstream.
Insoluble fibre is responsible for promoting regularity and helping to prevent constipation by speeding up the passage of food and waste through the intestines and absorbing water to keep stools soft. Insoluble fibre has been shown to reduce the risk of haemorrhoids.
Fibre-containing foods such as sweetcorn also help to provide a sense of satiety and may therefore help to suppress appetite and aid weight management.
Dietary fibre has also been linked to a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. A diet rich in fibre helps patients manage their disease.
Fibre is fermented by bacteria in the colon. Promising studies are underway to determine the health-promoting effects of fibre fermentation breakdown products, for example, short-chain fatty acids, which may help to maintain a healthy gut.

Yellow Sweet Corn,Double Packed Sweet Corn,Double Packed Sweet Corn Cob,Double Packed Yellow Sweet Corn
Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorns.com