Chromatography - Amino Acid Features
An amino acid is both acidic and basic, meaning that it contains both an acidic group (carboxylic acid) and a basic group (primary amine).
However, these groups are condensed with the residue by peptide bonds.
A plurality of amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to form a peptide chain.
The characteristics of the protein/polypeptide are determined by the amino acid side chain.
This article contains a detailed description and an overview of the features.
Includes amino acid names, three-letter abbreviations, and one-letter symbols.
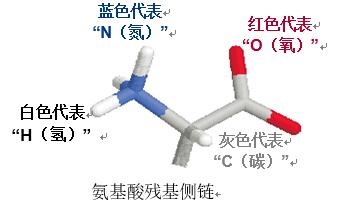
Amino acid | characteristic | structure |
Alanine Ala A | Type: Hydrophobic Function: The side chain consists of a hydrophobic methyl group. Like other hydrophobic amino acids, alanine assists in the formation and maintenance of the tertiary structure of the protein. |
|
Arginine Arg R | Type: Alkaline |
|
Asparagine Asn N | Type: weak polarity |
|
Aspartic acid Asp D | Type: Acidic Function: Aspartic acid has a pH of 4 and interacts with basic amino acids to form an electrostatic complex (salt bridge). |
|
Cysteine Cys C | Type: weak polarity (sulphur) Function: Cysteine ​​plays an important role in the tertiary structure of proteins, which react with other cysteine ​​side chains and form covalent bonds (disulfide bonds) in different parts of the polypeptide chain. |
|
Glutamine Gln Q | Type: weak polarity Function: Deamidation of glutamine is more difficult than asparagine, so it is not used as a deamidation site. |
|
Glutamate Glu E | Type: Acidic Function: The pH of glutamic acid is slightly higher than 4, and interacts with basic amino acids to form an electrostatic complex (salt bridge). |
|
Glycine Gly G | Type: Neutral |
|
Histidine His H | Type: Alkaline |
|
Isoleucine Ile I | Type: Hydrophobic |
|
Leucine Leu L | Type: Hydrophobic |
|
Lysine Lys K | Type: Alkaline |
|
Methionine Met M | Type: weakly hydrophobic (sulphur-containing) Function: Methionine is the most likely amino acid to be oxidized. It is an indicator of oxidation. Oxidation of methionine may also affect biological activity. |
|
Phenylalanine Phe F | Type: hydrophobic, aromatic |
|
Proline Pro P | Type: weakly hydrophobic |
|
Serine Ser S | Type: Polar (including hydroxyl) |
|
Threonine Thr T | Type: Polar (including hydroxyl) Function: Threonine binds to other amino acid residues or parts of proteins by hydrogen bonding. It can also bind to other proteins or groups through hydrogen bonding. |
|
Tyrosine Tyr Y | Type: Polar (including hydroxyl), aromatic Function: Tyrosine binds to other amino acid residues or parts of proteins by hydrogen bonding. It can also bind to other proteins or groups through hydrogen bonding. |
|
Tryptophan Trp W | Type: hydrophobic, aromatic |
|
Proline Val V | Type: Hydrophobic |
|
Â
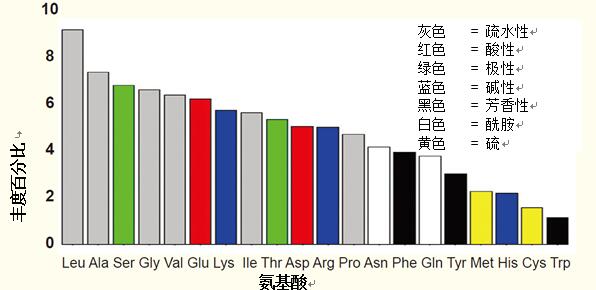
Abundance of individual amino acids <br> Hydrophobic amino acids play a key role in the formation of tertiary structures of proteins, usually located in the core of the protein.
They account for about 50% of the amino acids in the protein.
Polar amino acids have many important structural or functional effects, and abundance is generally high.
The least abundant amino acids include methionine, histidine, cysteine, and tryptophan.
Bioantibody Biotechnology Co., Ltd. , https://www.bioantibodymedical.com